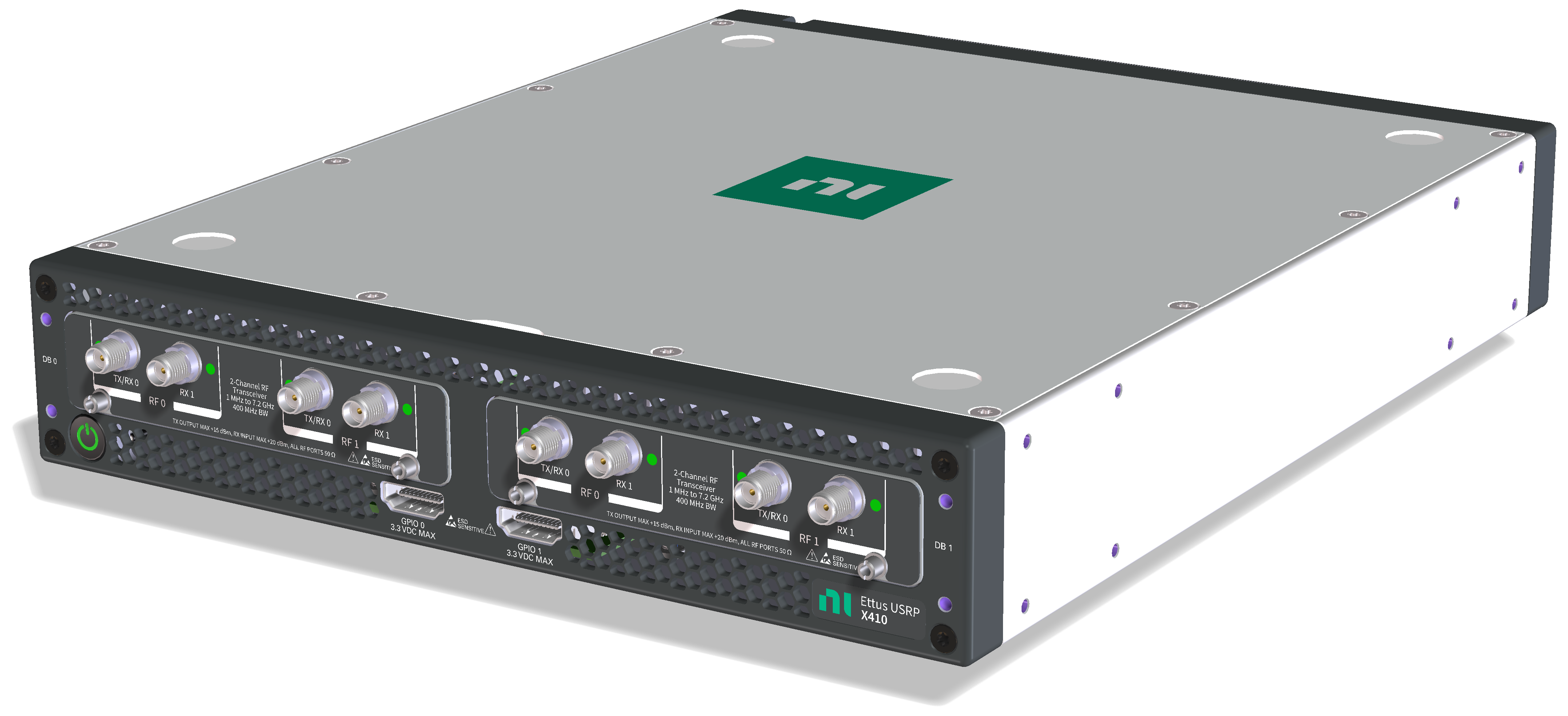

The Ettus USRP X410 is a fourth-generation Software Defined Radio (SDR) out of the USRP family of SDRs. It contains two ZBX Daughterboards for a total of 4 channels at up to 400 MHz of analog bandwidth each. The analog features of the ZBX Daughterboard are described in a separate manual page.
The USRP X410 features a Xilinx RFSoC, running an embedded Linux system. Like other USRPs, it is addressable through a 1 GbE RJ45 connector, which allows full access to the embedded Linux system, as well as data streaming at low rates. In addition, it features two QSFP28 connectors, which allow for up to 4x10 GbE or 1x100 GbE connections each.
The front panel provides access to the RF connectors (SMA), Tx/Rx status LEDs, programmable GPIOs, and the power button. The rear panel is where the power and data connections go (Ethernet, USB) as well as time/clock reference signals and GPS antenna.
X410's cooling system uses a field replaceable fan assembly and supports two variants: one that pulls air front-to-back and one that pulls air back-to-front. By default, the unit comes with the front-to-back fan assembly.
The main chip (the SoC) of the X410 is a Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ RFSoC (ZU28DR). It contains an ARM quad-core Cortex A53 CPU (referred to as the "APU"), an UltraScale+ FPGA including peripherals such as built-in data converters and SD-FEC cores, and an ARM Cortex-R5F real-time processor (the "RPU").
The programmable logic (PL, or FPGA) section of the SoC is responsible for handling all sampling data, the high-speed network connections, and any other high-speed utilities such as custom RFNoC logic. The processing system (PS, or CPU) is running a custom-built OpenEmbedded-based Linux operating system. The OS is responsible for all the device and peripheral management, such as running MPM, configuring the network interfaces, running local UHD sessions, etc.
The programmable logic bitfile contains certain hard-coded configurations of the hardware, such as what type of connectivity the QSFP28 ports use, and how the RF data converters are configured. That means to change the QSFP28 from a 10 GbE to a 100 GbE connection requires changing out the bitfile, as well as when reconfiguring the data converters for different master clock rates. See FPGA Image Flavors for more information.
It is possible to connect to the host OS either via SSH or serial console (see sections SSH Connection and Serial Connection, respectively).
The X410 has a higher maximum analog bandwidth than previous USRPs. It can provide rates up to 500 Msps, resulting in a usable analog bandwidth of up to 400 MHz. In order to facilitate the higher bandwidth, UHD uses a technology called Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK). See the DPDK page for details on how it can improve streaming, and how to use it.
The Ettus USRP X410 contains two ZBX daughterboards. To find out more about the capabilities of these analog front-end cards, see ZBX Daughterboard.
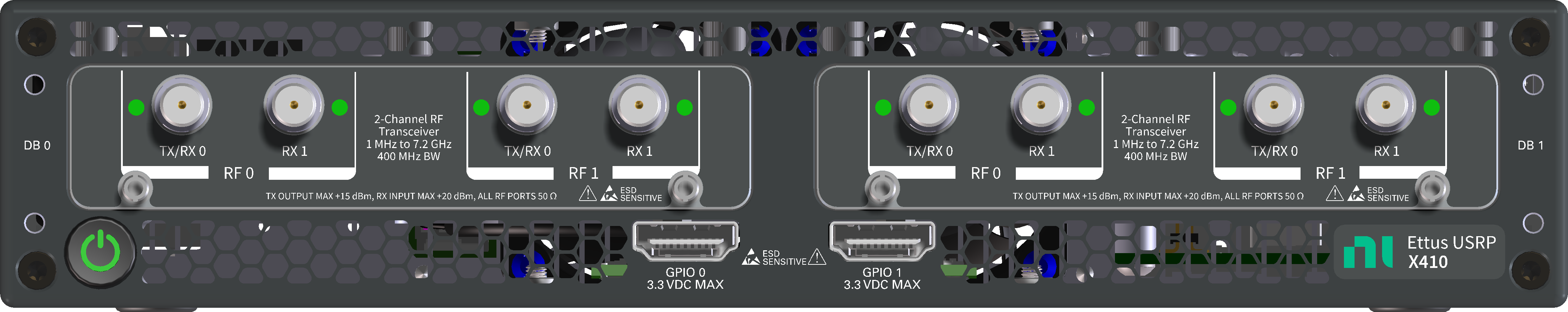

The front panel provides access to the RF ports and status LEDs of the ZBX Daughterboard. It also provides access to the front-panel GPIO connectors (2x HDMI) and the power button.
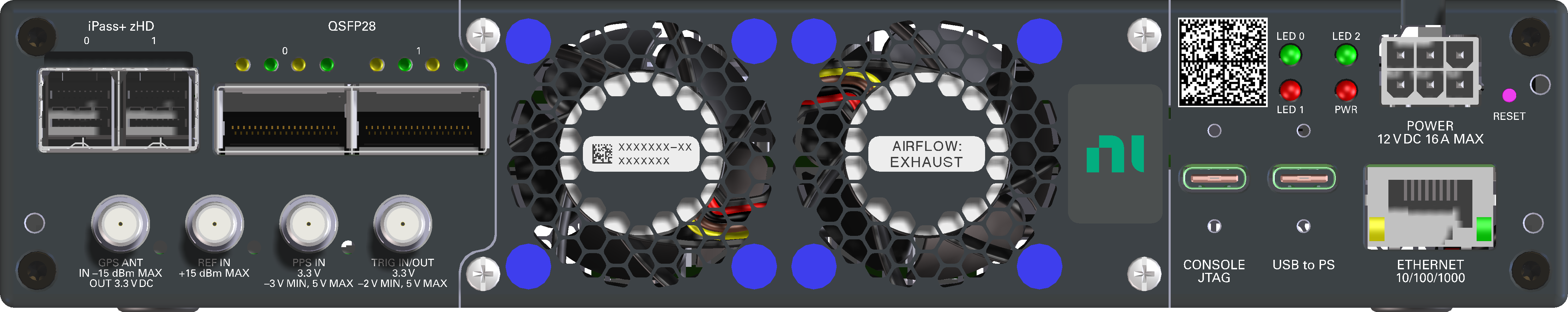
The back panel provides access to power, data connections, clocking and timing related connections, and some status LEDs:
The STM32 microcontroller (also referred to as the "SCU") controls various low-level features of the X4x0 series motherboard: It controls the power sequencing, reads out fan speeds and some of the temperature sensors. It is connected to the RFSoC via an I2C bus. It is running software based on Chromium EC.
It is possible to log into the STM32 using the serial interface (see Connecting to the Microcontroller). This will allow certain low-level controls, such as remote power cycling should the CPU have become unresponsive for whatever reason.
Coming soon!
The main non-volatile storage of the USRP is a 16 GB eMMC storage. This storage can be made accessible as a USB Mass Storage device through the USB-OTG connector on the back panel.
The entire root file system (Linux kernel, libraries) and any user data are stored on the eMMC. It is partitioned into four partitions:
Note: It is possible to access the currently inactive root file system by mounting it. After logging into the device using serial console or SSH (see the following two sections), run the following commands:
$ mkdir temp $ mount /dev/mmcblk0p3 temp # This assumes mmcblk0p3 is currently not mounted $ ls temp # You are now accessing the idle partition: bin data etc lib media proc sbin tmp usr boot dev home lost+found mnt run sys uboot var
The device node in the mount command might differ, depending on which partition is currently already mounted.
Firstly, download and install UHD on a host computer following Binary Installation or Building and Installing UHD from source. The USRP X410 requires UHD version 4.1 or above.
Inside the kit you will find the X410 and an X410 power supply. Plug these in, connect the 1GbE RJ45 interface to your network, and power on the device by pressing the power button.
Once the X410 has booted, determine the IP address and verify network connectivity by running uhd_find_devices on the host computer:
$ uhd_find_devices
--------------------------------------------------
-- UHD Device 0
--------------------------------------------------
Device Address:
serial: 1234ABC
addr: 10.2.161.10
claimed: False
mgmt_addr: 10.2.161.10
product: x410
type: x4xx
By default, an X410 will use DHCP to attempt to find an address.
At this point, you should run:
uhd_usrp_probe --args addr=<IP address>
to ensure functionality of the device.
Note: If you receive the following error:
Error: RuntimeError: Graph edge list is empty for rx channel 0
then you will need to download a UHD-compatible FPGA as described in Updating the FPGA or using the following command (it assumes that FPGA images have been downloaded previously using uhd_images_downloader, or that the command is run on the device itself):
uhd_image_loader --args type=x4xx,addr=<ip address>,fpga=X4_200
When running on the device, use 127.0.0.1 as the IP address.
You can now use existing UHD examples or applications (such as rx_sample_to_file, rx_ascii_art_dft, or tx_waveforms) or other UHD-compatible applications to start receiving and transmitting with the device.
See Network Interfaces for further details on the various network interfaces available on the X410.
The Ettus USRP X410 has various network interfaces:
eth0: RJ45 port.int0: internal interface for network communication between the embedded ARM processor and FPGA.169.254.0.1/24. This interface is agnostic of FPGA image flavor.sfpX [, sfpX_1, sfpX_2, sfpX_3]: QSFP28 network interface(s), up-to four (one per lane) based on implemented protocol.sfpXfor the first lane, and sfpX_1-3 for the other three lanes. Each network interface has a default static IP address. Note that for multi-lane protocols, such as 100 GbE, a single interface is used (sfpX).The configuration files for these network interfaces are stored in: /data/network/<interface>.network.
| Interface Name | Description | Default Configuration | Configuration File | Example: X4_200 FPGA image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
eth0 | RJ45 | DHCP | eth0.network | DHCP |
int0 | Internal | 169.254.0.1/24 | int0.network | 169.254.0.1/24 |
sfp0 | QSFP28 0 (4-lanes interface or lane 0) | 192.168.10.2/24 | sfp0.network | 192.168.10.2/24 |
sfp0_1 | QSFP28 0 (lane 1) | 192.168.11.2/24 | sfp0_1.network | 192.168.11.2/24 |
sfp0_2 | QSFP28 0 (lane 2) | 192.168.12.2/24 | sfp0_2.network | 192.168.12.2/24 |
sfp0_3 | QSFP28 0 (lane 3) | 192.168.13.2/24 | sfp0_3.network | 192.168.13.2/24 |
sfp1 | QSFP28 1 (4-lanes interface or lane 0) | 192.168.20.2/24 | sfp1.network | N/C |
sfp1_1 | QSFP28 1 (lane 1) | 192.168.21.2/24 | sfp1_1.network | N/C |
sfp1_2 | QSFP28 1 (lane 2) | 192.168.22.2/24 | sfp1_2.network | N/C |
sfp1_3 | QSFP28 1 (lane 3) | 192.168.23.2/24 | sfp1_3.network | N/C |
For example, /data/network/eth0.network by default looks like:
In order to change the eth0 interface from using DHCP to using a static IP, you can edit /data/network/eth0.network to be like:
replacing the IP address with the IP of your choice.
The Ettus USRP X410 is equipped with status LEDs for its network-capable ports: RJ45 and QSFP28s, see RJ45 LED Behavior and QSFP28 LED Behavior accordingly.
The RJ45 port has two independent LEDs: green (right) and yellow (left). The table below summarizes the LEDs' behavior. Note that link speed indication is not currently supported.
| Link / Activity | Green LED | Yellow LED |
|---|---|---|
| No Link | Off | Off |
| Link / No Activity | On | Off |
| Link / Activity | On | Blinking |
Each QSFP28 connector has four LEDs, one for each high-speed transceiver lane. The table below summarizes the LEDs' behavior, note that for multi-lane protocols, such as 100 GbE, the corresponding LEDs are ganged together. Within the same image, multiple speeds on the same port (e.g., both 10 GbE and 100 GbE) are not supported, therefore link speed indication is not supported.
| Link / Activity | QSFP28 LED (4 total) |
|---|---|
| No Link | Off |
| Link / No Activity | Green (solid) |
| Link / Activity | Amber (blinking) |
The X410 ships without a root password set. It is possible to ssh into the device by simply connecting as root, and thus gaining access to all subsystems. To set a password, run the command
$ passwd
on the device.
It is possible to gain access to the device using a serial terminal emulator. To do so, the USB debug port needs to be connected to a separate computer to gain access. Most Linux, OSX, or other Unix flavors have a tool called 'screen' which can be used for this purpose, by running the following command:
$ sudo screen /dev/ttyUSB2 115200
In this command, we prepend 'sudo' to elevate user privileges (by default, accessing serial ports is not available to regular users), we specify the device node (in this case, /dev/ttyUSB2), and the baud rate (115200).
The exact device node depends on your operating system's driver and other USB devices that might be already connected. Modern Linux systems offer alternatives to simply trying device nodes; instead, the OS might have a directory of symlinks under /dev/serial/by-id:
$ ls /dev/serial/by-id usb-Digilent_Digilent_USB_Device_2516351DDCC0-if02-port0 usb-Digilent_Digilent_USB_Device_2516351DDCC0-if03-port0
Note: Exact names depend on the host operating system version and may differ.
The first (with the if02 suffix) connects to the STM32 microcontroller (SCU), whereas the second (with the if03 suffix) connects to Linux running on the RFSoC APU.
$ sudo screen /dev/serial/by-id/usb-Digilent_Digilent_USB_Device_2516351DDCC0-if03-port0 115200
After entering the username root (no password is set by default), you should be presented with a shell prompt similar to the following:
root@ni-x4xx-1234ABC:~#
On this prompt, you can enter any Linux command available. Using the default configuration, the serial console will also show all kernel log messages (unlike when using SSH, for example), and give access to the boot loader (U-boot prompt). This can be used to debug kernel or bootloader issues more efficiently than when logged in via SSH.
The microcontroller (which controls the power sequencing, among other things) also has a serial console available. To connect to the microcontroller, use the other UART device. In the example above:
$ sudo screen /dev/serial/by-id/usb-Digilent_Digilent_USB_Device_2516351DDCC0-if02-port0 115200
It provides a very simple prompt. The command 'help' will list all available commands. A direct connection to the microcontroller can be used to hard-reset the device without physically accessing it and other low-level diagnostics. For example, running the command reboot will emulate a reset button press, resetting the state of the device, while the command powerbtn will emulate a power button press, turning the device back on again.
The USRP X4x0-Series devices have two network connections: The dual QSFP28 ports, and an RJ45 connector. The latter is by default configured by DHCP; by plugging it into into 1 Gigabit switch on a DHCP-capable network, it will get assigned an IP address and thus be accessible via ssh.
In case your network setup does not include a DHCP server, refer to the section Serial Connection. A serial login can be used to assign an IP address manually.
After the device obtained an IP address you can log in from a Linux or OSX machine by typing:
$ ssh root@ni-x4xx-1234ABC # Replace with your actual device name!
Depending on your network setup, using a .local domain may work:
$ ssh [email protected]
Of course, you can also connect to the IP address directly if you know it (or set it manually using the serial console).
Note: The device's hostname is derived from its serial number by default (ni-x4xx-$SERIAL). You can change the hostname by creating the file /data/network/hostname, saving the desired hostname in it, then rebooting.
On Microsoft Windows, the connection can be established using a tool such as PuTTY, by selecting a username of root without password.
Like with the serial console, you should be presented with a prompt like the following:
root@ni-x4xx-1234ABC:~#
The FPGA can be updated simply using uhd_image_loader:
uhd_image_loader --args type=x4xx,addr=<IP address of device> --fpga-path <path to .bit>
or
uhd_image_loader --args type=x4xx,addr=<IP address of device>,fpga=FPGA_TYPE
A UHD install will likely have pre-built images in /usr/share/uhd/images/. Up-to-date images can be downloaded using the uhd_images_downloader script:
uhd_images_downloader
will download images into /usr/share/uhd/images/ (the path may differ, depending on how UHD was installed).
Also note that the USRP already ships with compatible FPGA images on the device - these images can be loaded by SSH'ing into the device and running:
uhd_image_loader --args type=x4xx,mgmt_addr=127.0.0.1,fpga=X4_200
Unlike the USRP X310 or other third-generation USRP devices, the FPGA image flavors do not only encode how the QSFP28 connectors are configured, but also which master clock rates are available. This is because the data converter configuration is part of the FPGA image (the ADCs/DACs on the X410 are on the same die as the FPGA).
The image flavors consist of two short strings, separated by an underscore, e.g. X4_200 is an image flavor which contains 4x 10 GbE, and can handle an analog bandwidth of 200 MHz. The first few characters describe the configuration of the QSFP28 ports: 'X' stands for 10 GbE, 'C' stands for 100 GbE. The second group of characters indicates the analog bandwidth.
As of UHD 4.2, the following images flavors are shipped with UHD:
| FPGA Image Flavor | Bandwidth | QSFP28 Port 0 Interface | QSFP28 Port 1 Interface | DDC/DUC | DRAM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X4_200 | 200 MHz | 4x 10 GbE (All Lanes) | N/C | Yes | Yes (4-Ch Replay) |
| CG_400 | 400 MHz | 100 GbE | 100 GbE | No | No |
The following list shows some potential use-cases for different FPGA images:
X4_200: 200 MHz analog bandwidth, or below (using RFNoC DDC/DUCs), streaming between the X410 and an external host computer, or streaming to/from on-board DRAM using the RFNoC Record/Replay block.CG_400: Full-rate (400 MHz analog bandwidth) streaming between the X410 and an external host computer. The current implementation requires dual 100 GbE connections for 4 full-duplex channels or a single 100 GbE connection for 2 full-duplex channels.X4_400: Full-rate (400 MHz analog bandwidth) streaming to/from on-board DRAM using the RFNoC Record/Replay block. Up to 4 x 10 GbE connections may be used to access the DRAM from an external host computer. Note that 10 GbE is not fast enough for continuous full-rate streaming at this rate.Run make help in the fpga/usrp3/top/x400 directory of the UHD repository to see a complete list of FPGA images that can be built, some of which are experimental (unsupported).
The analog bandwidth determines the available master clock rates. The 200 MHz images allow master clock rates of 245.76 MHz or 250 MHz. The 400 MHz images allow master clock rates of 491.52 MHz or 500 MHz.
Applications that require more than 200 MHz bandwidth should use the full rate of the 400 MHz images. Applications that require 200 MHz bandwidth or less should use the 200 MHz images and make use the DDC/DUC for lower rates.
The USRP X410 has two banks of DDR4 memory available for use by the programmable logic in the FPGA. Each bank has a 4 GiB capacity. The DRAM can be run at up to 2.4 GT/s but is clocked at 2.0 GT/s by default to ease FPGA timing closure.
The FPGA memory controller exposes each bank of DRAM as a 512-bit interface clocked at 250 MHz. This interface is then presented to RFNoC as up to 4 AXI interfaces. For 200 MHz images, each AXI interface is 64-bit at 250 MHz. For 400 MHz images, each AXI interface is 128-bit at 250 MHz. This allows for the maximum sample rate to be read and written to DRAM for up to 4 channels simultaneously.
The default use for the DRAM is the Replay RFnoC block, which supports recording and playback of data in real time. See section FPGA Image Flavors for a list of which images have DRAM by default.
The easiest way to update the filesystem is directly from the X410 via the built-in usrp_update_fs utility.
To perform a filesystem "factory-reset", run:
$ usrp_update_fs
To update to the most-recent filesystem, run:
$ usrp_update_fs -t master
Note: Old filesystems may not support this utility. Alternatively, one may use Mender to update the filesystem. See Updating the Filesystem Using Mender.
Mender is a third-party software that enables remote updating of the root file system without physically accessing the device (see also the Mender website). Mender can be executed locally on the device, or a Mender server can be set up which can be used to remotely update an arbitrary number of USRP devices. Mender servers can be self-hosted, or hosted by Mender (see mender.io for pricing and availability).
When updating the file system using Mender, the tool will overwrite the root file system partition that is not currently mounted (note: the onboard flash storage contains two separate root file system partitions, only one is ever used at a single time). Any data stored on that partition will be permanently lost, including the currently loaded FPGA image. After updating that partition, it will reboot into the newly updated partition. Only if the update is confirmed by the user, the update will be made permanent. This means that if an update fails, the device will be always able to reboot into the partition from which the update was originally launched (which presumably is in a working state). Another update can be launched now to correct the previous, failed update, until it works.
To initiate an update directly from the X410 device, download a Mender artifact containing the update itself. These are files with a .mender suffix. They can be downloaded by using the uhd_images_downloader utility:
$ uhd_images_downloader -t mender -t x4xx
Append the -l switch to print out the URLs only:
$ uhd_images_downloader -t mender -t x4xx -l
By default, this utility will download the .mender artifact to /usr/share/uhd/images.
Note: uhd_images_downloader will only download the artifacts released with the currently installed filesystem version (factory-reset). To install the latest released filesystem version instead, first download the most-recent manifest from the UHD Github repository:
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EttusResearch/uhd/master/images/manifest.txt
Second, use the -m switch to use the new manifest file:
$ uhd_images_downloader -t mender -t x4xx -m manifest.txt
Once a Mender artifact is downloaded to the X410 (see Downloading a Mender Artifact), install it by running mender on the command line:
$ mender install /path/to/latest.mender
Alternatively, Mender may be used to download and install an artifact that is stored on a remote server, all in one step:
$ mender install http://server.name/path/to/latest.mender
This procedure will take a while. If the new filesystem requires an update to the MB CPLD, see Updating the Motherboard CPLD before proceeding. After mender has logged a successful update, reboot the device:
$ reboot
If the reboot worked, and the device seems functional, commit the changes so the boot loader knows to permanently boot into this partition:
$ mender commit
To identify the currently installed Mender artifact from the command line, the following file can be queried:
$ cat /etc/mender/artifact_info
If you are running a hosted server, the updates can be initiated from a web dashboard. From there, you can start the updates without having to log into the device, and can update groups of USRPs with a few clicks in a web GUI. The dashboard can also be used to inspect the state of USRPs. This is a simple way to update groups of rack-mounted USRPs with custom file systems.
In the event that the new system has problems booting, you can attempt to reset the boot environment using the following instructions.
First, connect to the USB serial console at a baud rate of 115200. Boot the device, and stop the boot sequence by typing noautoboot at the prompt. Then, run the following commands in the U-boot command prompt:
env default -a env save reset
The last command will reboot the USRP. If the / filesystem was mounted to mmcblk0p2 as described in Updating Filesystems, then stop the boot again and run:
run altbootcmd
Otherwise, let the boot continue as normal.
Caution! Updating the motherboard CPLD has the potential to brick your device if done improperly.
After updating the filesystem, you may have to update your motherboard CPLD. If you forget to update the CPLD, MPM will fail to fully initialize and emit a warning. This is not critical, and the CPLD update can be performed later by following these same steps, but the device will not be usable until then.
Even though the CPLD may not require updating, it is recommended to always run these steps for a consistent update procedure.
You can update the motherboard (MB) CPLD by running the following command on the X410:
x4xx_update_cpld --file=<path to cpld-x410.rpd>
Note: Old filesystems may not contain this command. If you are performing a mender update, simply run these commands after the update.
Filesystems will usually contain a compatible cpld-x410.rpd file at /lib/firmware/ni/cpld-x410.rpd. If you're installing a new filesystem via mender, you may have to mount the new filesystem (before you boot into it) in order to access the new firmware:
mkdir /mnt/other mount /dev/mmcblk0p3 /mnt/other cp /mnt/other/lib/firmware/ni/cpld-x410.rpd ~ umount /mnt/other
Note that the other filesystem may be either /dev/mmcblk0p2 or /dev/mmcblk0p3.
If x4xx_update_cpld returns an error, diagnose the error before proceeding.
After updating the MB CPLD, a power cycle is required for the changes to take effect. Shut down the device using:
shutdown -h now
and then un-plug, wait several seconds, then re-plug the power to the USRP.
Alternatively, in lieu of physical access, the microcontroller can be accessed using the USB serial port as described in Serial Connection, and can be used to reboot the device:
reboot powerbtn
Read this section if you want to create your own motherboard CPLD image.
The motherboard CPLD's source code can be found in the UHD source code repository under fpga/usrp3/top/x400/cpld.
Building the MB CPLD requires "Quartus 20.1.0 Standard Edition or
later". To generate the MB CPLD image, navigate to fpga/usrp3/top/x400/cpld and run:
make build
Read the Makefile in that directory for further details.
The writable SCU image file is stored on the filesystem under /lib/firmware/ni/ec-titanium-revX.RW.bin (where X is a revision compatibility number). To update, simply replace the .bin file with the updated version and reboot.
While Mender should be used for routine filesystem updates (see Updating Filesystems), it is also possible to access the X410's internal eMMC from an external host over USB. This allows accessing or modifying the filesystem, as well as the ability to flash the device with an entirely new filesystem.
In order to do so, you'll need an external computer with two USB ports, and two USB cables to connect the computer to your X410. The instructions below assume a Linux host.
First, connect to the APU serial console at a baud rate of 115200. Boot the device, and stop the boot sequence by typing noautoboot at the prompt. Then, run the following command in the U-boot command prompt:
ums 0 mmc 0
This will start the USB mass storage gadget to expose the eMMC as a USB mass storage device. You should see a spinning indicator on the console, which indicates the gadget is active.
Next, connect your external computer to the X410's USB to PS port using an OTG cable. Your computer should recognize the X410 as a mass storage device, and you should see an entry in your kernel logs (dmesg) that looks like this:
usb 3-1: New USB device found, idVendor=3923, idProduct=7a7d, bcdDevice= 2.23 usb 3-1: New USB device strings: Mfr=1, Product=2, SerialNumber=0 usb 3-1: Product: USB download gadget usb 3-1: Manufacturer: National Instruments sd 6:0:0:0: [sdc] 30932992 512-byte logical blocks: (15.8 GB/14.8 GiB) sdc: sdc1 sdc2 sdc3 sdc4 sd 6:0:0:0: [sdc] Attached SCSI removable disk
The exact output will depend on your machine, but from this log you can see that the X410 was recognized and /dev/sdc is the block device representing the eMMC, with 4 partitions detected (see eMMC Storage for details on the partition layout).
It is now possible to treat the X410's eMMC as you would any other USB drive: the individual partitions can be mounted and accessed, or the entire block device can be read/written.
Once you're finished accessing the device over USB, the u-boot gadget may be stopped by hitting Ctrl-C at the APU serial console.
Once the X410's eMMC is accessible over USB, it's possible to write the filesystem image using dd. You can obtain the latest filesystem image by running:
uhd_images_downloader -t sdimg -t x4xx
The output of this command will indicate where the downloaded image can be found.
Run:
sudo dd if=/path/to/usrp_x4xx_fs.sdimg of=/dev/sdX bs=1M
to flash the eMMC with this image (replacing /dev/sdX with the block device of the X410's eMMC as indicated by your kernel log).
When copying has completed, hit Ctrl-C on the U-boot prompt to terminate the mass storage mode. Then, power-cycle the device to load the new filesystem.
If the X410 is no longer able to boot from eMMC, it is possible to boot the device into u-boot over JTAG. This will allow the filesystem to be reflashed using the process described in USB Access to eMMC.
In order to boot the X410 over JTAG, you'll first need to have either the Xilinx SDK, or the freely available Vivado Lab Edition. The following steps require that one of these is installed and available in your environment.
For convenience, pre-compiled bootloader binaries are provided, along with a script to handle downloading these into the X410's memory and booting the device. These are included in the sdimg package with the name usrp_x4xx_recovery.zip, which can be downloaded using:
uhd_images_downloader -t sdimg -t x4xx
To boot the device over JTAG, first ensure the X410 is powered off, and that you have serial consoles open to both the SCU and the APU. Configure the device to boot over JTAG by running zynqmp bootmode jtag on the SCU console, and press the power button (or run the powerbtn command at the SCU console). At this point, the device is powered on and the APU is held in reset.
Run xsdb boot_u-boot.tcl in the directory where you've extracted the bootloader binaries. This will download the various binaries needed to boot the device into memory, and bring the APU out of reset. Once this script completes, you should see u-boot loading on the APU serial console. From here, you can follow the steps in USB Access to eMMC to reflash the eMMC.
After the eMMC has been flashed, run reboot at the SCU console to reset the device and return back to the default boot mode. A subsequent press of the power button will boot the device from the eMMC.
Like any other USRP, all X4x0 USRPs are controlled by the UHD software. To integrate a USRP X4x0 into your C++ application, you would generate a UHD device in the same way you would for any other USRP:
For a list of which arguments can be passed into make(), see Section Device Arguments.
| Key | Description | Example Value |
|---|---|---|
| addr | IPv4 address of primary SFP+ port to connect to. | addr=192.168.30.2 |
| second_addr | IPv4 address of secondary SFP+ port to connect to. | second_addr=192.168.40.2 |
| mgmt_addr | IPv4 address or hostname to which to connect the RPC client. Defaults to ‘addr’. | mgmt_addr=ni-x4xx-311FE00 |
| find_all | When using broadcast, find all devices, even if unreachable via CHDR. | find_all=1 |
| master_clock_rate | Master Clock Rate in Hz. | master_clock_rate=250e6 |
| serialize_init | Force serial initialization of motherboards (default is parallel) | serialize_init=1 |
| skip_init | Skip the initialization process for the device. | skip_init=1 |
| time_source | Specify the time (PPS) source. | time_source=internal |
| clock_source | Specify the reference clock source. | clock_source=internal |
| ref_clk_freq | Specify the external reference clock frequency, default is 10 MHz. | ref_clk_freq=20e6 |
| discovery_port | Override default value for MPM discovery port. | discovery_port=49700 |
| rpc_port | Override default value for MPM RPC port. | rpc_port=49701 |
The USRP X410 includes a Jackson Labs LTE-Lite GPS module. Its antenna port is on the rear panel (see Front and Back Panels). When the X410 has access to GPS satellite signals, it can use this module to read out the current GPS time and location as well as to discipline an onboard OCXO.
To use the GPS as a clock and time reference, simply use gpsdo as a clock or time source. Alternatively, set gpsdo as a synchronization source:
Note the GPS module is not always enabled. Its power-on status can be queried using the gps_enabled GPS sensor (see also The Sensor API). When disabled, none of the sensors will return useful (if any) values.
When selecting gpsdo as a clock source, the GPS will always be enabled. Note that acquiring a GPS lock can take some time after enabling the GPS, so if a UHD application is enabling the GPS dynamically, it might take some time before a GPS lock is reported.
The USRP X410 has two HDMI front-panel connectors, which are connected to the FPGA. For a description of the GPIO control API, see X4x0 GPIO API.
There are multiple sources that can control the state of the GPIO lines. UHD has the capability of controlling which source each pin is driven from. The source control block is located in the X4x0 core logic block in the FPGA, and is also accessible via MPM. There are also local registers in the source control block that control the state of GPIOs manually if none of the additionally supported control schemes are required.
Source selection is performed via an array of muxes, each accessible via an independent register. The diagram below indicates the arrangement of muxes controlling GPIO source selection.
UHD has access to all radio-controlled blocks. In the diagram above, this includes one ATR DIO control block and one digital interface block for each radio.
When ATR control is selected as the source, it uses the Daughterboard state to determine the behavior of the GPIOs. The Daughterboard state is the concatenation of the transmission state of all channels in the daughterboard.
The Digital Interface Block currently supports a variable rate SPI bus. Having one of these blocks for each radio grants the ability to have two SPI engines running simultaneously. Each engine has the ability to service multiple slaves, but transactions can only be issued to one slave at a time. Slaves are customizable, and clock rate, instruction length, edge polarity are accommodated for based on the currently selected slave. Mapping of SPI signals to DIO port pins is also customizable. See The x4x0 SPI Mode.
Mapping from any source to the front-panel connectors is performed in a per-pin basis, allowing the user to interact with each connector pin from any radio.
The RF ports on the front panel of the X410 + ZBX correspond to the following subdev specifications:
| Label | Subdev Spec |
|---|---|
| DB 0 / RF 0 | A:0 |
| DB 0 / RF 1 | A:1 |
| DB 1 / RF 0 | B:0 |
| DB 1 / RF 1 | B:1 |
The subdev spec slot identifiers "A" and "B" are not reflected on the front panel. They were set to match valid subdev specifications of previous USRPs, maintaining backward compatibility.
These values can be used for uhd::usrp::multi_usrp::set_rx_subdev_spec() and uhd::usrp::multi_usrp::set_tx_subdev_spec() as with other USRPs.
Like other USRPs, the X4x0 series have daughterboard and motherboard sensors. For daughterboard sensors, cf. Sensors.
When using uhd::usrp::multi_usrp, the following API calls are relevant to interact with the motherboard sensor API:
The following motherboard sensors are always available:
ref_locked: This will check that all the daughterboards have locked to the external reference.temp_fpga: The temperature of the RFSoC die itself.temp_main_power: The temperature of the PM-BUS devices which supply 0.85V to the RFSoC.temp_scu_internal: The internal temperature reading of the STM32 microcontroller.fan0: Fan 0 speed (RPM).fan1: Fan 1 speed (RPM).The GPS sensors will return empty values if the GPS is inactive (note it may be inactive when using a different clock than gpsdo, see also GPS). There are two types of GPS sensors. The first set requires an active GPS module and is acquired by calling into gpsd on the embedded device, which in turn communicates with the GPS via a serial interface. For this reason, these sensors can take a few seconds before returning a valid value:
gps_time: GPS time in seconds since the epoch.gps_tpv: A TPV report from GPSd serialized as JSON.gps_sky: A SKY report from GPSd serialized as JSON.gps_gpgga: GPGGA string.The seconds set of GPS sensors probes pins on the GPS module. They are all boolean sensors values. If the GPS is disabled, they will always return false.
gps_enabled: Returns true if the GPS module is powered on.gps_locked: Returns the state of the 'LOCK_OK' pin.gps_alarm: Returns the state of the 'ALARM' pin.gps_warmed_up: Returns the state of the 'WARMUP_TRAINING' pin. Indicates warmup phase, can be high for minutes after enabling GPS.gps_survey: Returns the state of the 'SURVEY_ACTIVE' pin. Indicates state of auto survey process. Indicates that module is locked to GPS, and that there are no events on the GPS module pending.The USRP X410 is equipped with four LEDs located on the device's rear panel. Each LED supports four different states: Off, Green, Red, and Amber. One LED (PWR) indicates the device's power state (see Power LED below). The other three LEDs (LED 0, LED 1, and LED 2) are user-configurable, different behaviors are supported for each of these LEDs (see User-configurable LEDs below).

The USRP X410's PWR LED is reserved to visually indicate the user the device's power state. Power LED Behavior describes what each LED state represents.
PWR LED State | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Off | No power is applied |
| Amber | Power is good but X410 is powered off |
| Green | Power is good and X410 is powered on |
| Red | Power error state |
The USRP X410's user-configurable rear panel status LEDs (LED 0, LED 1, and LED 2) allow the user to have visual indication of various device conditions. Supported LED Behaviors provides a complete list of the supported behaviors for each user-configurable LED. By default, these LEDs are configured as described in LEDs Default Behavior.
The user may alter the default LEDs behavior either temporarily or persistently, see Temporarily change the LED Behavior or Persistently change the LED Behavior accordingly.
activity: flash green LED for CPU activityemmc: flash green LED for eMMC activityheartbeat: flash green LED with a heartbeatfpga: change LED to green when FPGA is loadednetdev <interface>: green LED indicates interface link, amber indicates activity<interface> is the name of any network interface (e.g. eth0)none: LED is constantly offpanic: red LED turns on when kernel panicsuser0: off, green, red or amber LED state is controlled by FPGA application, see Using FPGA LED Controluser1: off, green, red or amber LED state is controlled by FPGA application, see Using FPGA LED Controluser2: off, green, red or amber LED state is controlled by FPGA application, see Using FPGA LED Control| LED Number | Default Behavior |
|---|---|
| LED 0 | heartbeat |
| LED 1 | fpga |
| LED 2 | emmc |
A user may change the X410 LEDs' default behavior via running a utility on the on-board ARM processor (Linux).
ledctrl utility to configure each LED based on desired supported behavior: ledctrl <led> <command>Where
<led> valid options are: led0, led1, and led2. These options correspond to the rear panel labels. The <command> valid options are listed in the Supported LED Behaviors section above, with their corresponding description.Example:
root@ni-x4xx-1111111:~# ledctrl led0 user0
Sets the X410's LED 0 to be controlled via the FPGA application using "User LED 0".
The above method will not persist across reboots. In order to persist the changes, modify the ledctrl service unit files which are run by the init system at boot. These files can be found on a running filesystem at, e.g., /lib/systemd/system/ledctrl-led0.service.
When selecting user0, user1, and/or user2 as LED behavior (see Supported LED Behaviors above), the FPGA application gains control of that given LED. The following paragraph describes how the FPGA application can control the state for each setting.
FPGA application access to User LED 0-2 requires modification of the FPGA source code and is achieved directly via Verilog, using a 2-bit vector to control the state.
Below is an excerpt of the FPGA source code, setting the user0, user1, and user2 values to green, red, and amber respectively.
The USRP X410 has three processors on the motherboard: The RFSoC, the SCU, and a control CPLD. The RFSoC does the bulk of the work. It houses the programmable logic (PL), the APU and RPU processors (the former running the embedded Linux system), connects to the data ports (RJ45, QSFP28) and also includes RF data converters (ADC/DAC) which are exposed to the daughterboards through a connector. The FPGA configuration for the RFSoC can be found in the source code repository under fpga/usrp3/top/x400. The OpenEmbedded Linux configuration can be found on a separate repository.
The SCU is a microcontroller running a baremetal control stack. It controls the power sequencing, the fan speeds, connects various peripherals and sensors to the Linux kernel, and performs other low-level tasks. It can be accessed through a serial console directly from the back-panel. This can be a useful debugging tool if the device is not responding to other inputs, and can be used to power-cycle and reboot the USRP. It is connected to the RFSoC using an I2C interface.
The motherboard control CPLD performs various control tasks, such as controlling the clocking card and the GPIO connectors (note that the GPIO pins are also available without using the CPLD, which is the normal case when programming the pins for an application with higher rates and precise timing). The motherboard CPLD is accessible from the RFSoC through a SPI interface, and also acts as a SPI mux for accessing peripherals such as the clocking card. Access to the motherboard CPLD from within a UHD session always goes through MPM, meaning it is not used for high-speed or high-precision control. Its source code can be found in the UHD source code repository under fpga/usrp3/top/x400/cpld.
The RJ45 Ethernet connector is connected directly to the PS and is made available in Linux as a regular Ethernet interface. It is possible to stream data to and from the FPGA, but the data is tunneled through the operating system, which makes it a relatively slow interface. The QSFP28 connectors are directly connected to the RFSoC transceivers. Different FPGA images configure these either as 10 GbE or 100 GbE interfaces. It is possible to access the PS through these interfaces (when configured as Ethernet interfaces), but their main purpose is to stream data from and to the FPGA at high rates.
The clocking architecture of the motherboard is spread out between a clocking auxiliary board, which contains an OCXO (either GPS-disciplined or controlled by a DAC), but also connects an external reference to the motherboard. Furthermore, it houses a PLL for deriving a clock from the network (eCPRI).
The motherboard itself has two main PLLs for clocking purposes: The Sample PLL (also SPLL) is used to create all clocks used for RF-related purposes. It creates the sample clock (a very fast clock, ~3 GHz) and the PLL reference clock (PRC) which is used as a reference for the LO synthesizers (50-64 MHz).
Its input is called the base reference clock (BRC). It has four possible sources:
internal, this OCXO is only disciplined by a DAC (control of that DAC is not exposed in this version of UHD), but there is no further control loop. By selecting gpsdo as a clock source, a GPS module is used to discipline the OCXO (see also GPS).external as the clock source), the X410 assumes a 10 MHz reference clock (it is possible to drive the device with a different external clock frequency by providing the ref_clk_freq device argument, but this is not a supported use case for this UHD version). Note the clocking card can also import a PPS signal (when setting the time source to external) as well as export it.nsync clock source). It will generate a 10 MHz BRC. Note the intention is to use this for scenarios where the clock is derived from the network port (e.g., eCPRI), but this version of UHD does not include such a feature.mboard (this is a 25 MHz BRC). This is not a common use case, as it is not possible to synchronize the on-board clock. This is the only clock that does not come from the auxiliary clocking board.The reference PLL (RPLL) produces clocks that are consumed by the GTY banks (for Ethernet), as well as the on-board BRC. By default, its reference is a fixed 100 MHz clock, but it can also be driven by the eCPRI PLL.
The eCPRI PLL is typically driven by a clock derived from the GTY banks, which is the assumption if the clock source is set to 'nsync'. The eCPRI PLL can also be driven from the RFSoC ("fabric clock") for testing purposes.
The master clock rate (MCR) depends on the sample clock rate. It also depends on the RFDC settings, which are different for different flavours of FPGA images (see also FPGA Image Flavors). The actual clock running at this frequency is generated digitally, within the RFSoC, and is derived from the SPLL clock.
Block diagram:
Note that this section does not cover every single clock signal present on the X410, but mainly those clock signals relevant for the operation of the RF components. Refer to the schematic for more details.